Starting or growing a business in Australia often needs financial support. Whether you’re opening a café in Sydney, expanding a construction company in Brisbane, or buying new farm equipment in regional Victoria, business loans can help you get the capital you need.
But many business owners still ask — how do business loans work?
In this complete and easy-to-understand guide, we’ll explain everything — from the meaning and process to examples and loan calculations — so you can make smart financial decisions for your business.
🏦 What Is a Business Loan?
A business loan is a type of financing that allows business owners to borrow money from a bank, credit union, or online lender.
You borrow a fixed amount (called the principal) and repay it with interest over an agreed period (called the loan term).
It’s different from a personal loan because the lender looks at your business’s financial strength, not just your personal credit score.
🔹 Example
Imagine your small bakery in Melbourne needs AUD 50,000 to buy new ovens and renovate the shop.
You apply for a business loan, and the bank approves it for 3 years at 8% interest per annum.
You’ll repay the loan in monthly instalments that include both principal and interest.
💡 Why Businesses in Australia Take Loans
Australian businesses use loans for different reasons. Here are the most common:
| Purpose | Example |
| Working Capital | Covering daily expenses like wages, bills, and rent |
| Equipment Purchase | Buying machines, vehicles, or tools |
| Business Expansion | Opening a new branch or increasing production |
| Marketing and Growth | Running advertising campaigns |
| Debt Consolidation | Combining multiple loans into one manageable payment |
| Seasonal Demands | Managing cash flow in off-seasons |
🏷️ Types of Business Loans in Australia
Australian lenders offer a range of business loans to suit different needs. Let’s understand the main types:
1. Term Loans
You receive a lump sum and repay it over a fixed term with interest.
- Can be short-term (under 12 months) or long-term (3–10 years).
- Offered by banks like Commonwealth Bank, NAB, ANZ, and Westpac.
📘 Example:
You borrow AUD 100,000 at 9% annual interest for 5 years.
You’ll pay back both the loan and interest monthly over 60 months.
2. Business Line of Credit
It works like a credit card. You get access to a set limit, draw funds when needed, and pay interest only on what you use.
📘 Example:
If you have a AUD 50,000 line of credit and use AUD 20,000, you pay interest only on AUD 20,000, not the full limit.
3. Secured vs. Unsecured Loans
| Type | Description | Example |
| Secured Loan | Backed by collateral (like property, vehicle, or equipment). Lower interest. | Loan secured against your delivery van. |
| Unsecured Loan | No collateral needed, but higher interest. | A new business loan without assets. |
4. Equipment Finance
If you need machinery, vehicles, or IT systems, this loan lets you purchase or lease equipment while paying it off gradually.
📘 Example:
You get AUD 80,000 for new printing machines. The machines themselves act as collateral.
5. Invoice Financing
For businesses waiting on client payments, invoice financing allows you to borrow money against unpaid invoices to maintain cash flow.
6. Merchant Cash Advance
You receive funds upfront and repay the loan through a percentage of your daily card sales.
This is popular among retail shops and cafés.
📊 How Do Business Loans Work Step-by-Step
Here’s the simple process of how business loans work in Australia:
Step 1: Determine Your Need
Decide why you need the loan — for cash flow, expansion, or new equipment.
Step 2: Check Eligibility
Lenders look at:
- Business credit score
- Annual revenue
- Time in operation
- Existing debts
- Business plan and purpose of funds
Step 3: Compare Lenders
Compare interest rates, fees, repayment options, and loan terms from:
- Major banks (CBA, NAB, ANZ, Westpac)
- Non-bank lenders (Prospa, Moula, OnDeck, Bizcap)
Step 4: Apply Online or In-Person
Provide your ABN, financial statements, bank statements, tax returns, and ID proof.
Step 5: Loan Approval
If approved, funds are transferred to your business account — often within a few days for online lenders.
Step 6: Repayment
You’ll make regular repayments (weekly, fortnightly, or monthly) with interest.
📈 Understanding Interest and Repayments
Let’s see how business loan repayment works with a real calculation.
🧮 Example Calculation:
You borrow AUD 100,000 at 8% annual interest for 5 years (60 months).
Use the standard loan formula:
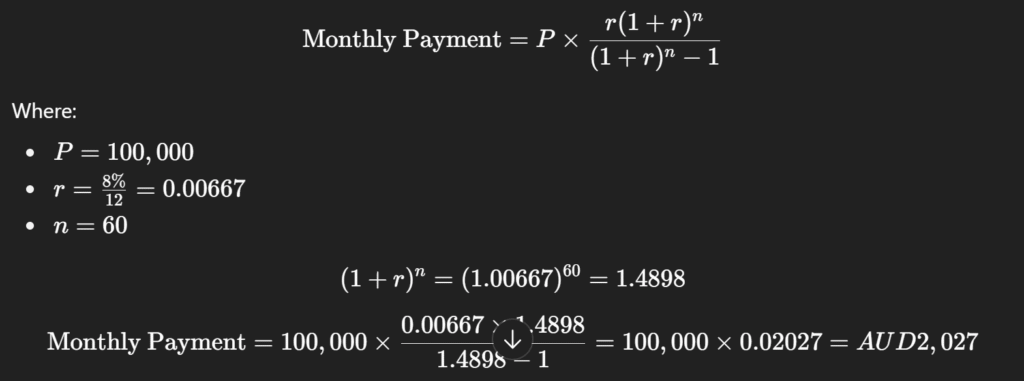
✅ Monthly repayment: AUD 2,027
✅ Total repayment over 5 years: 2,027 × 60 = AUD 121,620
✅ Total interest paid: AUD 21,620
So, by borrowing AUD 100,000, you’ll repay AUD 121,620 in total.
🧾 Flat vs. Reducing Interest
- Flat interest means you pay interest on the original amount for the whole term.
- Reducing balance means interest is calculated on the remaining loan balance — this is fairer and cheaper over time.
Most Australian banks use reducing balance for business loans.
🧠 Factors That Affect Business Loan Approval
Before lending money, Australian lenders check several key things:
| Factor | Why It Matters |
| Credit Score | Shows how responsibly you’ve handled past debts |
| Business Age | Startups are riskier, so older businesses get better rates |
| Cash Flow Stability | Strong, steady cash flow means lower default risk |
| Collateral | Valuable security reduces lender’s risk |
| Industry Type | Some sectors (like construction or hospitality) are higher risk |
| Loan Purpose | Lenders want to know how funds will help the business grow |
⚖️ Advantages and Disadvantages of Business Loans
✅ Pros
- Keeps your business ownership (no investors needed)
- Interest payments are tax deductible
- Improves business credit rating
- Helps you grab growth opportunities quickly
- Predictable repayments help with financial planning
❌ Cons
- You must repay even if business income drops
- Can be expensive for small or new businesses
- Missed payments hurt your credit score
- Some loans require personal guarantees or collateral
💬 Example Scenario: Comparing Two Loan Options
| Details | Bank A | Lender B |
| Loan Amount | AUD 100,000 | AUD 100,000 |
| Interest Rate | 8% | 10% |
| Loan Term | 5 years | 5 years |
| Monthly Payment | AUD 2,027 | AUD 2,125 |
| Total Interest | AUD 21,620 | AUD 27,500 |
Even though 2% may seem small, over time you save AUD 5,880 by choosing the cheaper loan.
That’s why comparing lenders before borrowing is crucial.
🧾 Tax Benefits of Business Loans in Australia
- Interest paid on business loans is usually tax-deductible as a business expense.
- Equipment bought using loans can qualify for instant asset write-off under ATO rules.
- Always check with a tax accountant to confirm eligibility.
📘 Example:
If your business pays AUD 10,000 in loan interest in a year, and your company tax rate is 25%,
you could save AUD 2,500 in taxes.
🧩 Government Support and SME Loan Schemes
In Australia, several government-backed programs help small businesses access finance:
- SME Recovery Loan Scheme — supported by the Australian Government and major banks.
- Export Finance Australia (EFA) — supports exporters and international trade.
- Regional Investment Corporation (RIC) — offers concessional loans for farmers.
- State Government Grants — each state has small business funding programs.
These programs often offer lower interest rates or longer repayment periods.
💬 Tips Before Applying for a Business Loan
- Check your credit report for any errors.
- Prepare updated financial statements and cash flow forecasts.
- Borrow only what you truly need.
- Compare at least 3 lenders before deciding.
- Read all terms carefully — especially fees and penalties.
- Understand if the loan is secured or unsecured.
- Plan how the loan will improve revenue or efficiency.
💰 Alternative Financing Options
If a traditional loan doesn’t fit, consider these:
- Crowdfunding (e.g. Kickstarter, GoFundMe)
- Angel Investors or Venture Capital
- Invoice Factoring
- Peer-to-Peer Lending Platforms
- Business Credit Cards
These may offer flexibility but can have different risks and costs.
📘 Key Takeaways
| Concept | Summary |
| Definition | Business loans help fund operations, expansion, or equipment. |
| Types | Term loan, line of credit, secured/unsecured, equipment finance. |
| Interest | Usually reducing balance; interest depends on risk and term. |
| Repayment | Monthly instalments over fixed term. |
| Eligibility | Based on credit, income, and business health. |
| Benefits | Ownership retained, tax benefits, faster growth. |
| Risks | Must repay even in slow periods; may require collateral. |
Also Read: Finance Tips and Tricks Build Your Wealth Through Debt
🏁 Conclusion: Smart Borrowing Leads to Business Growth
Understanding how business loans work in Australia helps you borrow wisely, avoid surprises, and use funds for real growth.
A business loan is not just money — it’s a strategic tool that can help your business reach new milestones when used carefully. Always plan repayments, compare lenders, and ensure the borrowed funds generate more income than the cost of interest.
With the right planning, business loans can turn your vision into reality — whether that’s expanding your store, upgrading equipment, or launching a new product.










