Finance and mathematics are deeply connected. Whether you are saving money, taking a loan, investing in stocks, or planning for retirement, you are using math every single time. Many people think finance is difficult, but when concepts are explained in simple language with examples, it becomes very easy to understand.
In this long, informative blog, you will learn how is math used in finance, understand important formulas, and see step-by-step examples using dollars. By the end, you will clearly understand how numbers help in making smart financial decisions.
What Is Financial Mathematics?
Financial mathematics means using math to solve money-related problems. It helps in:
- Calculating interest
- Understanding loans
- Estimating investment returns
- Measuring risk
- Deciding between financial options
Banks, investors, businesses, loan companies, insurance companies, and even individuals use financial math every day. Without math, it would be impossible to run the financial world.
Why Math Is Important in Finance
Math allows you to make decisions based on facts and numbers, not guesswork. It helps you know:
- How much your savings will grow
- How much interest you will pay on a loan
- Whether an investment is profitable
- How much risk you are taking
- What your future money will be worth
Let’s understand this with real examples in dollars.
Key Concepts: How Is Math Used in Finance
Below are the most important concepts, each explained in simple language with examples.
Compound Interest
Compound interest is interest on your money + the interest already earned. It is the heart of finance.
Formula
A=P×(1 + r)^n
Where:
- A = Final amount
- P = Initial amount
- r = Interest rate
- n = Number of years
Example 1 (Simple & Clear)
You invest $1,000 at 6% interest for 3 years.
A=1000×(1 + 0.06)^3
A=1000×1.191016=$1,191.02
So, after 3 years you will have $1,191.02.
Present Value and Future Value
Money today is more valuable than the same amount in the future because you can invest it.
Future Value Example
You want to know how much $2,000 will become in 5 years, at 7% interest.
FV=2000×(1.07)^5 = 2000 x 1.40255=$2,805.10
Present Value Example
You will receive $5,000 after 3 years.
Interest rate = 5%
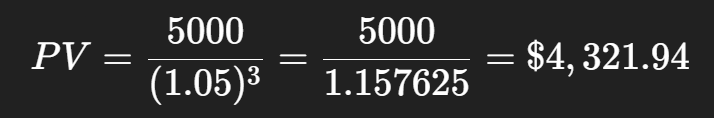
So, $5,000 after 3 years is worth $4,321.94 today.
Annuities (Series of Payments)
An annuity is a series of equal payments—like monthly savings or loan installments.
Formula
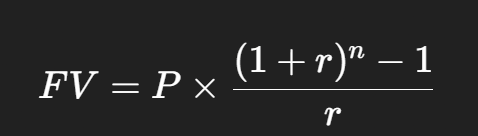
Example: Saving $100 per month
Monthly saving = $100
Interest = 8% per year, monthly = 0.00667
Years = 5 years = 60 months
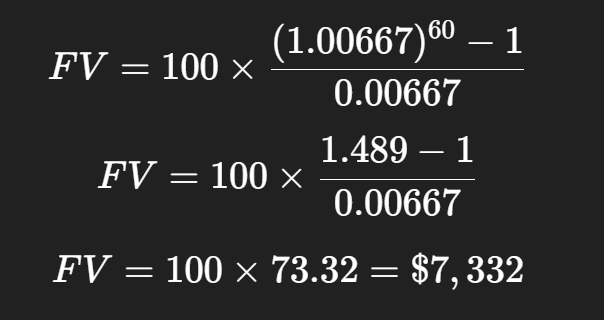
So, saving $100 per month gives you $7,332 in 5 years.
Probability and Statistics in Finance
Finance involves risk. Statistics helps predict outcomes.
Example
A stock has two possible returns:
- +12% return → probability 60%
- –5% return → probability 40%
Expected Return:
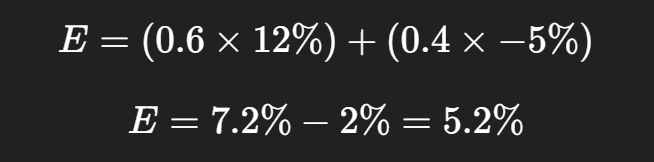
Average expected return = 5.2%
Risk Measurements
Standard deviation, correlation, and variance are used to measure:
- How risky an investment is
- How much returns fluctuate
- How different assets move together
These help investors manage uncertainty.
Where Math is Used in Real Financial Life
Math is used everywhere. Here are clear examples.
Banking
Banks use math to:
- calculate loan interest
- set EMI payments
- determine mortgage affordability
- calculate savings returns
Example: Loan Interest Calculation
You take a $10,000 loan at 8% interest for 2 years.
Simple interest estimate:
Interest=P×r×t=10000×0.08×2=1600
Total repayment = $11,600
But banks usually compound interest monthly, making the cost slightly higher.
Investments
Investment math is used to:
- value stock portfolios
- calculate returns
- compare assets
- estimate future profit
Example: Stock Return
You buy a stock for $50 and sell it for $65 after 1 year.
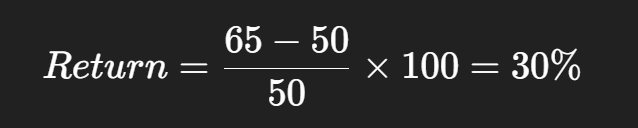
So you earned 30% return.
Retirement Planning
Planning long-term goals requires math.
Example: Saving $300 per month for 25 years
Interest = 7% yearly (0.583% monthly)
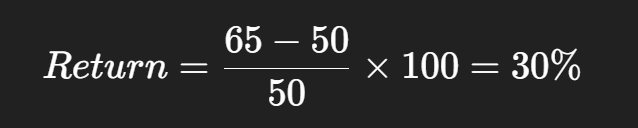
You will have $122,370 at retirement.
Budgeting
Math helps you organize:
- earnings
- expenses
- savings
- debts
Example
Monthly income = $3,000
Expenses = $2,200
Savings = $800 per month = $9,600 per year
Large Combined Example: Full Lifetime Calculation
Let’s combine everything into one detailed scenario.
Scenario
You are 30 years old.
You want $1,000,000 at age 60 for retirement.
You can invest $400 per month at 8% yearly.
Let’s check if you will reach your goal.
Step 1: Calculate Monthly Rate
8% per year → monthly rate:
r=0.08/12=0.006666
Step 2: Number of Months
30 years × 12 = 360 months
Step 3: Use Annuity Formula
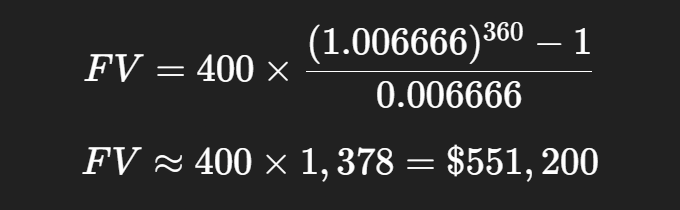
Final Result
You will have $551,200 — you need to increase your savings or investment returns to reach $1,000,000.
This example shows how math helps plan your financial future.
Common Mistakes in Financial Math
1. Ignoring Compounding
Small differences in compounding frequency change total results.
2. Forgetting Inflation
$1 today ≠ $1 in 20 years.
3. Assuming Returns Will Always Be the Same
Markets fluctuate. Use realistic expectations.
4. Not Understanding Loan Terms
Interest, APR, and compounding can change the cost heavily.
5. Overlooking Risk
High return = usually high risk.
Useful Formulas (Quick Reference Table)
| Concept | Formula | Explanation |
| Future Value | Growth of one amount | |
| Present Value | Today’s value of future money | |
| Annuity Future Value | Saving regularly | |
| Return | Profit percentage | |
| Expected Return | Average weighted return |
How Math Helps You Make Better Financial Decisions
- You can decide whether a loan is affordable.
- You can compare investment options.
- You can find out how much to save for retirement.
- You can estimate future costs like college, home, or travel.
- You can set a clear budget and long-term goals.
With math, money becomes predictable and manageable.
Also Read: What Is the Meaning of Finance?
Conclusion
Math is the backbone of finance. From compound interest to risk measurement, calculations help you understand how money grows, how loans work, and how to plan for the future. With simple formulas and clear examples like the ones in this blog, anyone can learn to make smarter financial decisions.
Finance becomes easy when you understand the numbers behind it.
The more comfortable you are with financial math, the stronger your financial future will be.










