When you take a loan—whether it’s for a car, home, or education—you agree to pay back the money you borrowed, plus interest. But did you know that the loan term you choose can change the total cost of your loan?
In simple words, the loan term is the length of time you’ll take to repay the loan. It could be short (like 3 years) or long (like 30 years). The length of this term directly affects your monthly payments, total interest paid, and overall cost of credit.
Let’s understand how do loan terms affect the cost of credit deeply with examples, easy calculations, and practical tips so you can make smarter financial decisions.
🏦 What Are Loan Terms?
Loan terms refer to all the conditions of a loan, such as:
- Loan amount (the money you borrow)
- Interest rate (percentage you pay for borrowing)
- Repayment period (the number of months or years)
- Monthly payment amount
- Fees and penalties (processing fees, prepayment charges, etc.)
In most cases, the most important part is the loan length, also called the loan term.
For example:
- A 30-year mortgage has smaller monthly payments but costs more in total interest.
- A 15-year mortgage has higher monthly payments but saves you thousands in total cost.
So, choosing the right term is a balance between monthly affordability and total interest cost.
📉 How Loan Term Affects Monthly Payments
The longer the loan term, the lower your monthly payments will be—because the total amount is divided into more months.
The shorter the loan term, the higher your monthly payments—because you repay the loan faster.
Let’s look at a clear example:
Example 1: $20,000 Car Loan at 6% Interest
| Loan Term | Monthly Payment | Total Interest | Total Paid |
| 36 months (3 years) | $608.44 | $1,903.84 | $21,903.84 |
| 60 months (5 years) | $386.66 | $3,199.52 | $23,199.52 |
👉 Result:
By choosing a longer 5-year term, you pay $1,295.68 more in interest compared to the 3-year term.
Why it happens:
Because with a longer term, your principal remains unpaid for more time, so the bank charges interest over a longer period.
💵 How Do Loan Terms Affect the Cost of Credit?
The total cost of credit means how much you pay in total—including the amount borrowed plus interest and fees.
The longer you take to pay back your loan, the more interest you’ll pay overall.
Let’s compare two different home loans to see the difference.
Example 2: $300,000 Mortgage at 6.5% Interest
| Loan Term | Monthly Payment | Total Interest | Total Paid |
| 20 years | $2,232.65 | $235,836 | $535,836 |
| 30 years | $1,896.20 | $382,632 | $682,632 |
👉 Result:
A 30-year loan costs you $146,796 more in interest than a 20-year loan.
Even though your monthly payment is lower, the total cost of credit becomes much higher.
Lesson:
Longer loan terms reduce short-term pressure but increase long-term costs.
📈 How Loan Terms Affect Interest Rates
Loan term and interest rate are connected. Usually:
- Short-term loans = Lower interest rates
- Long-term loans = Higher interest rates
Why?
Because lenders take a bigger risk by giving you money for a longer time. Over 10, 20, or 30 years, inflation, job loss, or market changes may affect your ability to pay. So, banks charge higher rates to cover that risk.
Example 3: $10,000 Personal Loan
| Loan Term | Interest Rate | Monthly Payment | Total Interest | Total Paid |
| 3 years | 9% | $318.15 | $1,453 | $11,453 |
| 5 years | 12% | $222.44 | $3,346 | $13,346 |
👉 Result:
Extending the loan term increases the interest rate and total cost, even though the monthly payment is smaller.
🧾 Detailed Calculation: How Term Changes Total Interest
Let’s calculate the total interest on two different loan terms using a simple example.
Example 4: $50,000 Loan at 7% Interest
Option 1: 5-Year Term
- Monthly payment = $990.06
- Total paid = $990.06 × 60 = $59,403.60
- Total interest = $9,403.60
Option 2: 10-Year Term
- Monthly payment = $580.54
- Total paid = $580.54 × 120 = $69,664.80
- Total interest = $19,664.80
👉 Result:
The 10-year loan costs you over $10,000 more in interest.
Even though the monthly payment is smaller, the overall cost is almost double in interest.
📊 Comparison Table: Short-Term vs Long-Term Loans
| Feature | Short-Term Loan | Long-Term Loan |
| Monthly Payment | Higher | Lower |
| Total Interest | Lower | Higher |
| Interest Rate | Usually Lower | Usually Higher |
| Time in Debt | Short | Long |
| Risk of Default | Lower | Higher |
| Total Cost of Credit | Lower | Higher |
Quick takeaway:
Short-term loans save money but require higher monthly payments.
Long-term loans are easier monthly but much more expensive overall.
💡 Why Longer Terms Feel Cheaper (But Are Not)
Many borrowers choose longer terms because the monthly payments “look” affordable. But that can be a trap.
For example, if you buy a car for $25,000 at 6% interest:
| Term | Monthly Payment | Total Paid | Total Interest |
| 36 months | $760.55 | $27,380 | $2,380 |
| 72 months | $414.89 | $29,847 | $4,847 |
👉 You save $345 monthly, but you pay $2,467 more in interest.
So while your wallet feels lighter each month, your overall spending is heavier in the long run.
🏠 Real-Life Example: Home Loan Impact
Let’s look at how the term affects a real mortgage.
Example 5: $400,000 Mortgage at 7% Interest
| Term | Monthly Payment | Total Paid | Total Interest |
| 15 years | $3,595 | $647,100 | $247,100 |
| 30 years | $2,661 | $958,000 | $558,000 |
👉 Result:
A 30-year loan costs you over $310,000 more in interest.
Even though your monthly payment is about $934 less, the long-term cost is huge.
This shows how important it is to think beyond the monthly bill.
🔍 How Loan Type Affects Term and Cost
Different loans have different typical terms:
| Loan Type | Common Term | Interest Range | Example |
| Personal Loan | 1 – 7 years | 8% – 18% | Borrow $10,000 for 5 years at 10% |
| Auto Loan | 3 – 7 years | 5% – 10% | Borrow $25,000 for 6 years at 7% |
| Student Loan | 10 – 25 years | 4% – 8% | Borrow $40,000 for 15 years at 6% |
| Mortgage | 15 – 30 years | 5% – 7.5% | Borrow $300,000 for 30 years at 6.5% |
Observation:
The longer the term, the smaller the monthly payment—but the more you pay in total.
💬 How to Choose the Best Loan Term
Here are some tips to help you decide what’s best for you:
1. Check Your Monthly Budget
If you can afford higher monthly payments comfortably, a shorter term will save you a lot of money.
2. Compare Total Costs, Not Just Payments
Always calculate how much total interest you’ll pay, not just how much per month.
3. Think About Your Income Stability
If your income is steady, shorter terms are better.
If uncertain, a longer term might offer flexibility.
4. Watch Interest Rate Differences
Longer terms often have higher interest rates. Check both before deciding.
5. Avoid Extending Just for Comfort
Don’t stretch your loan to 7 years just to lower monthly payments by $50—it could cost you thousands more.
6. Use a Loan Calculator
Online loan calculators (like Credible or PowerFi) can show how changing terms affect your cost instantly.
7. Make Extra Payments
If your loan allows it, paying a little extra each month can reduce both term and total interest.
🧮 Bonus: Simple Formula to Estimate Interest
For a quick estimate (without complex math):
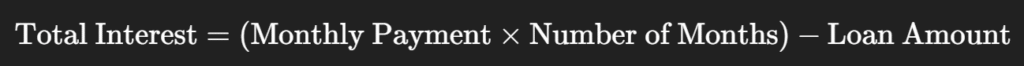
Example: $20,000 loan, $386.66 per month for 60 months
→ Total Interest = ($386.66 × 60) – $20,000 = $3,199.60
This simple formula helps you see the extra amount you pay for credit.
⚖️ Pros and Cons Summary
| Category | Short-Term Loan | Long-Term Loan |
| ✅ Advantage | Pay off faster, less interest | Lower monthly payments |
| ❌ Disadvantage | Higher monthly payment | More total interest, longer debt |
| 💡 Best For | People who can afford higher payments | People needing low monthly payments |
📘 Practical Example: Two Borrowers Compared
Borrower A and Borrower B both take a $30,000 car loan at 6% interest.
| Borrower | Term | Monthly Payment | Total Paid | Total Interest |
| A | 3 years (36 mo) | $912.66 | $32,855.76 | $2,855.76 |
| B | 6 years (72 mo) | $497.69 | $35,832.88 | $5,832.88 |
👉 Borrower B saves $415 monthly but pays $2,977 more in total.
Borrower A finishes paying in 3 years and saves nearly $3,000.
🪙 Smart Borrowing Tips to Reduce Loan Cost
- Choose the shortest term you can afford.
The faster you repay, the less interest you pay. - Pay extra whenever possible.
Even $50 extra a month can cut months off your loan term. - Improve your credit score.
A better score helps you get lower interest rates. - Compare multiple lenders.
Use online tools to check offers. - Avoid refinancing into longer terms unless necessary.
Refinancing might lower your payment but can increase total cost.
🧠 Key Takeaways
- Longer loan terms lower your monthly payments but increase total cost.
- Shorter terms increase your monthly payments but save thousands in interest.
- Always compare total interest paid, not just monthly payments.
- Interest rate and loan term are closely linked.
- Choose a term that balances comfort today and savings tomorrow.
Also Read: Tax Deductions for Remote Workers 2026 – Complete Guide
🏁 Conclusion
Your loan term plays a huge role in how much your credit actually costs.
A short-term loan helps you save money on interest and get out of debt faster.
A long-term loan reduces monthly stress but increases your total cost of credit.
Before signing any loan agreement, always ask these three questions:
- What is the total amount I will pay back?
- How much of that is interest?
- Can I afford a shorter term to save more?
By understanding how loan terms affect the cost of credit, you can borrow wisely, save thousands of dollars, and stay financially strong in the long run.










