When someone applies for a loan—whether it’s a small personal loan, a business loan, or even a mortgage—the lender doesn’t just look at your income. They want to know how safe it is to lend you money. To do this, they check five important factors known as the 5 Cs in finance.
So, what are the 5 Cs in finance of credit are Character, Capacity, Capital, Collateral, and Conditions.
Banks, credit unions, and financial institutions use them to decide if a borrower is trustworthy and financially stable.
In this blog, we’ll explain each “C” in simple words, show you how it works, and give clear examples with calculations in dollars.
By the end, you’ll know exactly how lenders think—and how you can improve your chances of getting approved for any loan.
🔹 What Are the 5 Cs in Finance?
The 5 Cs of Finance or 5 Cs of Credit are:
- Character – Your credit history and trustworthiness.
- Capacity – Your ability to repay the loan.
- Capital – The money you have invested or your savings.
- Collateral – Assets pledged against the loan.
- Conditions – The purpose of the loan and external market factors.
Each of these five elements gives lenders a different view of your financial profile.
Let’s explore each of them in detail.
🧾 1. Character – Your Credit Reputation
Definition:
“Character” tells how trustworthy you are as a borrower. Lenders look at your credit history, credit score, payment behavior, and job stability.
It’s all about your reputation for paying back loans on time.
Why It Matters:
Even if you earn well, a poor credit history (like missed payments or defaults) can make a lender hesitate. They want to lend money to someone responsible.
Example:
Let’s say two people apply for a loan of $10,000:
| Applicant | Credit Score | Late Payments | Job Stability | Likely Interest Rate |
| Alice | 780 | 0 | 5 years | 8% |
| Bob | 580 | 4 in last year | Frequent job changes | 14% |
👉 Even though both need $10,000, Alice gets a lower interest rate because of her good “Character.”
How to Improve:
- Pay all your bills and credit cards on time.
- Don’t apply for too many loans at once.
- Keep your oldest credit account active.
- Check your credit report for errors.
💰 2. Capacity – Your Ability to Repay
Definition:
“Capacity” measures your income compared to your debts. It helps the lender understand if you can afford monthly payments.
The most common measure is the Debt-to-Income (DTI) Ratio:

Example Calculation:
Sarah earns $6,000 per month and already pays $1,200 for her car loan and credit cards.
She wants a new personal loan with a monthly payment of $800.
So,
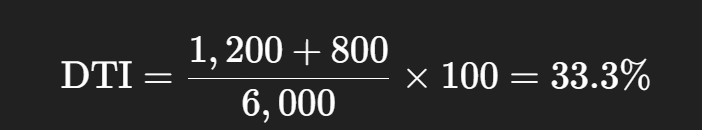
👉 A DTI below 40% is usually considered good.
That means Sarah has enough capacity to take the new loan.
For Businesses:
Lenders use the Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR):

If a company earns $250,000 annually and has total debt payments of $100,000,
DSCR=250,000/100,000=2.5
✅ A DSCR above 1.2 is usually healthy.
How to Improve:
- Pay down existing debt.
- Increase your income or side business earnings.
- Choose longer repayment terms to reduce monthly payments.
🏦 3. Capital – The Money You Invest
Definition:
“Capital” means how much of your own money you’re investing or how many assets you already have.
It shows your commitment and financial strength.
If you’re applying for a business loan, capital means the funds you’ve already put into your company.
If you’re applying for a personal loan, it means your savings or down payment.
Example 1: Home Loan
Suppose you want to buy a house worth $200,000.
| Down Payment | Loan Amount | Capital Contribution | Risk Level |
| $40,000 | $160,000 | 20% | Low |
| $10,000 | $190,000 | 5% | High |
👉 A higher down payment means you have more “Capital” at stake.
The bank sees this as less risky and may offer a lower interest rate.
Example 2: Business Loan
A startup wants to buy new equipment worth $100,000.
The owner contributes $25,000 and asks for a $75,000 loan.
This means they are investing 25% of their own money, which builds lender confidence.
How to Improve:
- Save before borrowing.
- Reinvest profits into your business.
- Avoid borrowing 100% of the project cost.
🧱 4. Collateral – Security for the Loan
Definition:
“Collateral” is an asset you pledge to the lender in case you can’t repay the loan.
It can be real estate, vehicles, equipment, or even savings accounts.
If you default, the lender can sell the collateral to recover the money.
That’s why secured loans (like car or home loans) have lower interest rates.
Example 1: Car Loan
Suppose you buy a car worth $25,000.
The lender allows an 80% Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio.
Loan Amount=25,000×80%=20,000
You’ll pay $5,000 as a down payment, and the car itself becomes the collateral.
If you fail to pay, the bank can repossess and sell the car.
Example 2: Business Collateral
A small business applies for a $100,000 loan.
They offer equipment worth $150,000 as collateral.
The bank sets an LTV of 70%.
Loan Eligibility=150,000×70%=105,000\text{Loan Eligibility} = 150,000 \times 70\% = 105,000Loan Eligibility=150,000×70%=105,000
✅ The loan request is safe and well covered by collateral value.
How to Improve:
- Keep records of your assets and ownership papers.
- Maintain your assets properly (servicing, insurance).
- Use high-value, easily sellable assets as collateral.
📊 5. Conditions – The Environment Around the Loan
Definition:
“Conditions” refer to why you need the loan and the economic situation affecting repayment.
It includes interest rates, inflation, job market, and your industry’s health.
Lenders also consider the loan purpose—buying a home, funding a business, or paying for education.
Example:
Let’s say two small businesses each request a $200,000 loan.
| Business | Industry | Purpose | Market Condition | Loan Approval |
| Company A | Healthcare | Expansion | Growing | ✅ Approved |
| Company B | Retail | Expansion | Declining | ❌ Risky |
Even if both have the same income, the economic conditions favor Company A.
Interest Rate Impact Example:
If the base rate is 7% and the economy is strong, the lender might charge 7.5%.
But if inflation rises or the industry is risky, the rate could increase to 9% or more.
How to Improve:
- Borrow during stable economic times.
- Clearly explain how the loan will be used.
- Show how market trends favor your project.
🔍 How the 5 Cs Work Together
The 5 Cs of Finance are connected.
No single “C” alone decides your fate; lenders see the whole picture.
Example Combination:
| C | Score | Comment |
| Character | Excellent | Credit score 770 |
| Capacity | Good | DTI 35% |
| Capital | Fair | 10% down payment |
| Collateral | Strong | Asset value = loan value |
| Conditions | Stable | Industry growing |
✅ Overall: Loan Approved at 8% interest.
Now suppose your Capacity is weak (DTI = 55%), but you have high Collateral (house value $400,000 for a $200,000 loan).
👉 The lender might still approve but at a higher interest rate (say, 10%) to cover risk.
Key takeaway:
Each “C” can balance another.
Good Collateral can offset weaker Character.
Strong Capacity can balance lower Capital.
🧮 Full Example – The 5 Cs in Action
Let’s understand with a full example:
Scenario:
Mr. John runs a small bakery and wants a $100,000 loan to open a second branch.
1. Character:
John has a credit score of 740 and has never missed payments. ✅
2. Capacity:
His bakery earns $12,000 per month.
Current monthly debt = $2,000.
New loan monthly payment = $1,800.
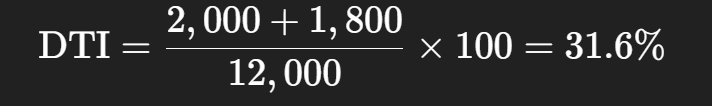
✅ Great capacity.
3. Capital:
He is investing $30,000 of his own money.
Loan-to-project ratio = 100,000 / (100,000 + 30,000) = 76.9% ✅ Good.
4. Collateral:
He pledges baking equipment worth $120,000.
LTV = 100,000 / 120,000 = 83% ✅ Acceptable.
5. Conditions:
Food industry is growing, interest rates are steady, and local economy is healthy. ✅
💡 Result:
All five Cs are positive → Loan approved at 8% interest rate for 5 years.
What If:
If John’s credit score was 600 and DTI 55%, the lender might still approve but at 11–12% interest and shorter tenure (3 years).
🧠 Why the 5 Cs Matter
For Borrowers
- You can prepare better before applying for a loan.
- Helps identify your weak areas (like high debt or low savings).
- Increases your chance of approval and reduces loan cost.
For Lenders
- Provides a structured way to measure risk.
- Ensures fair and consistent loan decisions.
- Helps set correct loan limits and interest rates.
✅ Tips to Improve Your 5 Cs
| C | Tips to Improve |
| Character | Pay bills on time, avoid unnecessary loans, check your credit score regularly. |
| Capacity | Reduce other debts, increase income, choose longer repayment terms. |
| Capital | Save more before borrowing, invest in assets, show financial discipline. |
| Collateral | Offer high-value, insured assets; maintain them well. |
| Conditions | Apply during favorable economic times; clearly define your loan purpose. |
⚠️ Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Thinking collateral alone is enough: Lenders also care about your repayment ability.
- Applying for loans without checking DTI: Always calculate your monthly obligations.
- Low down payment: The smaller your contribution, the higher your interest rate.
- Ignoring market risks: If your industry is unstable, strengthen other Cs before applying.
🧩 The 5 Cs Formula Summary
| Factor | What It Measures | Formula / Example |
| Character | Credit history & score | FICO 700+ = good |
| Capacity | Debt-to-income ratio | DTI = Total debt / Income × 100 |
| Capital | Personal investment | Down payment % |
| Collateral | Asset pledged | LTV = Loan / Asset value × 100 |
| Conditions | Purpose & economy | Strong market = better terms |
Also Read: 5 Practical Ways to Shape Your Financial Wellness
Conclusion
The 5 Cs in Finance — Character, Capacity, Capital, Collateral, and Conditions — are the five pillars that lenders use to judge a borrower’s creditworthiness.
They provide a complete picture of your financial health and ability to repay.
If you’re planning to apply for a loan, analyze yourself using these five Cs.
Work on improving your credit score, maintaining steady income, saving for a larger down payment, and offering strong collateral.
Remember, lenders don’t just see numbers — they see your financial behavior and commitment.
When you build all five Cs strongly, you not only increase your chances of loan approval but also secure lower interest rates and better terms.










